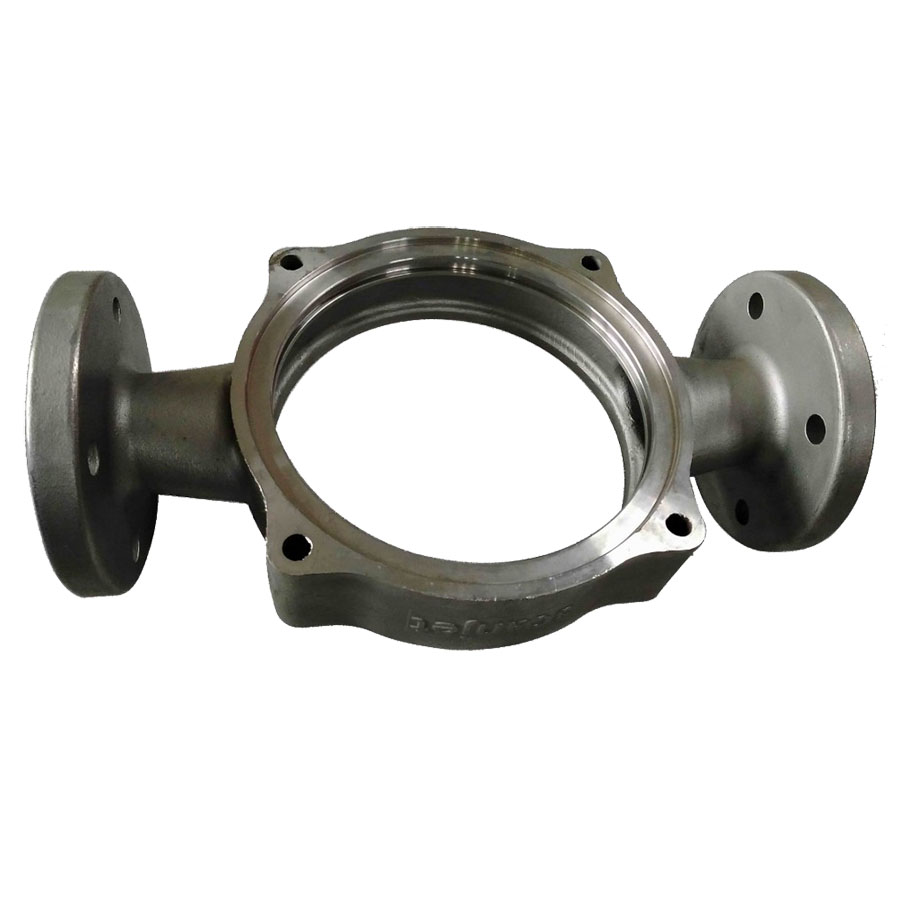

Stainless Steel Valve Housing by Investment Casting and Machining
Material: Stainless Steel AISI 316, AISI 304, 304L, 316L Process: Investment Casting + CNC Machining Weight: 2.50 kg Application: Valve Housing
OEM custom stainless steel valve housing by lost wax investment casting process. The 3.1 material certificate could be provided according to EN 10204.
Investment Casting Stainless Steel Valve Housing with CNC Precision Machining Services
Stainless steel valve spare parts are usually cast by investment casting process with silica solution as the binder materials for making the casting moulds.
Investment casting, which is also known lost wax casting or precision casting, refers to the formation of ceramic around the wax patterns to create a multi or single part mold to receive molten metal. This process utilizes an expendable injection molded wax pattern process to achieve complex forms with exceptional surface qualities. To create a mold, a wax pattern, or cluster of patterns, is dipped into ceramic material several times to build a thick shell. De-wax process is then followed by the shell dry process. The wax-less ceramic shell is then produced. Molten metal is then poured into the ceramic shell cavities or cluster, and once solid and cooled, the ceramic shell is broken off to reveal the final cast metal object. Precision investment castings can achieve exceptional accuracy for both small and large casting parts in a wide range of materials.

Inches
Millimeters
Dimension
Tolerance
Dimension
Tolerance
Up to 0.500
±.004"
Up to 12.0
± 0.10mm
0.500 to 1.000”
±.006"
12.0 to 25.0
± 0.15mm
1.000 to 1.500”
±.008"
25.0 to 37.0
± 0.20mm
1.500 to 2.000
±.010"
37.0 to 50.0
± 0.25mm
2.000 to 2.500
±.012"
50.0 to 62.0
± 0.30mm
2.500 to 3.500
±.014"
62.0 to 87.0
± 0.35mm
3.500 to 5.000
±.017"
87.0 to 125.0
± 0.40mm
5.000 to 7.500
±.020"
125.0 to190.0
± 0.50mm
7.500 to 10.000
±.022"
190.0 to 250.0
± 0.57mm
10.000 to 12.500
±.025"
250.0 to 312.0
± 0.60mm
12.500 to 15.000
±.028"
312.0 to 375.0
± 0.70mm
Excutive Standard of Casting Tolerance: ISO 8062 2013, ISO 2768, GOST 26645 (Russia) or GBT 6414 (China). Dimensional Casting Tolerances Grade (DCTG): 4 ~6 and Geometrical Casting Tolerances Grade (GCTG): 3 ~ 5.
As a precision casting process, the shell making is a very critical process during investment casting. The quality of the shell is directly related to the roughness and dimensional tolerance of the final casting. Therefore, it is an important task for the investment casting foundry to choose a suitable manufacturing method for the mold shell.
According to different adhesives, investment casting molds can be divided into water glass adhesive shells, silica sol adhesive shells, ethyl silicate adhesive shells and ethyl silicate-silica sol composite shells. These modeling methods are the most commonly used methods in investment casting.
Water Glass Shell
The investment casting produced by the water glass shell casting has high surface roughness, low dimensional accuracy, short shell-making cycle and low price. This process is widely used in casting carbon steel, low alloy steel, aluminum alloy and copper alloy.
Silica Sol Shell
The silica sol investment casting has low roughness, high dimensional accuracy, and long shell-making cycle. This process is widely used in high-temperature heat-resistant alloy castings, heat-resistant steel castings, stainless steel castings, carbon steel castings, low alloy castings, aluminum alloy castings and copper alloy castings.
Ethyl Silicate Shell
In investment casting, castings made by using ethyl silicate as a binder to make the shell have low surface roughness, high dimensional accuracy, and a long shell-making cycle. This process is widely used in heat-resistant alloy castings, heat-resistant steel castings, stainless steel castings, carbon steel castings, low alloy castings, aluminum alloy castings and copper alloy castings.

The Advantages of Investment Casting:
- Excellent and smooth surface finish
- Tight dimensional tolerances.
- Complex and intricate shapes with design flexibility
- Capability to cast thin walls therefore a lighter casting component
- Wide selection of cast metals and alloys (ferrous and non-ferrous)
- Draft is not required in the molds design.
- Reduce the need for secondary machining.
- Low material waste.
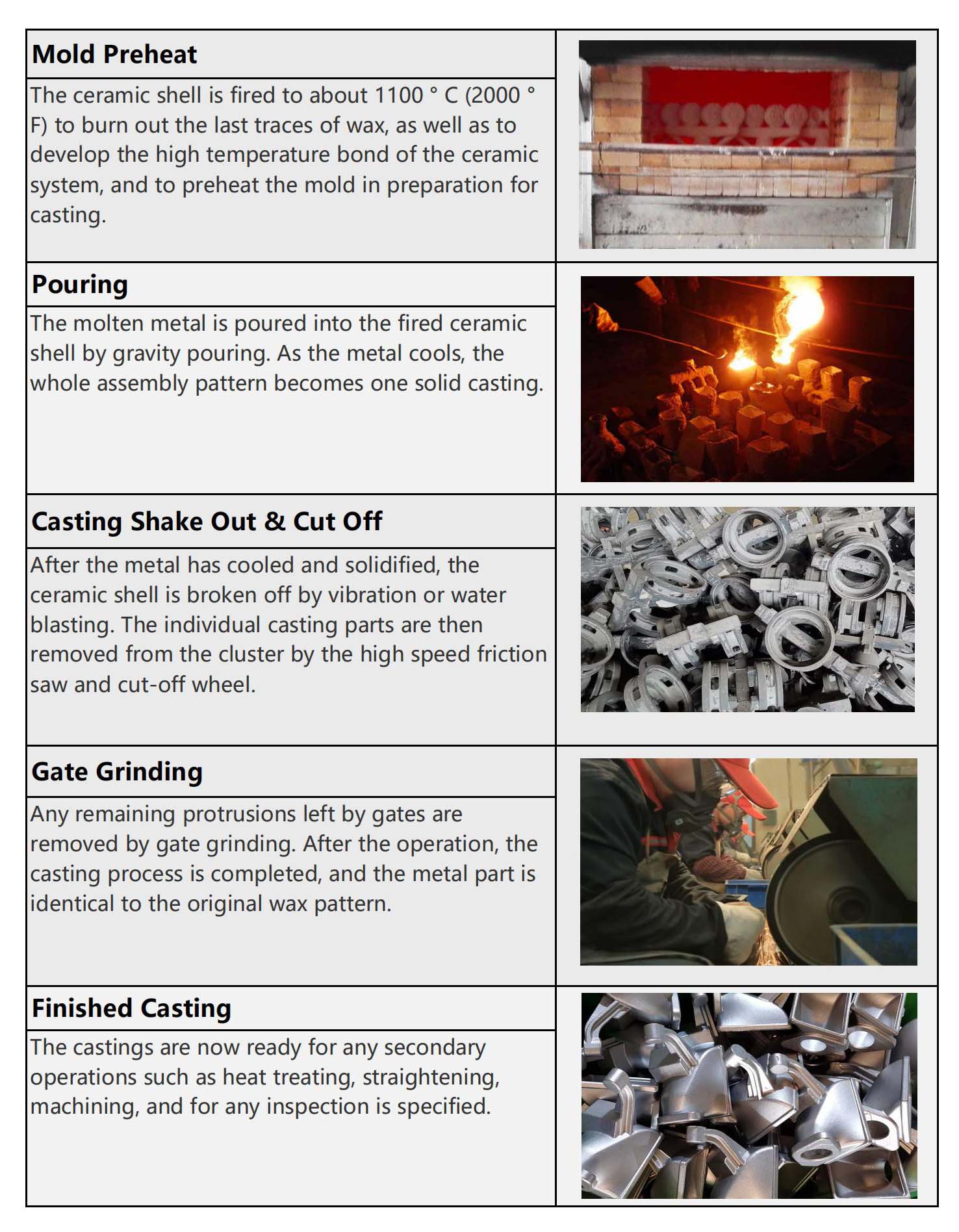
The Steps of Investment Casting Process:
During the investment casting process, a wax pattern is coated with a ceramic material, which, when hardened, adopts the internal geometry of the desired casting. In most cases, multiple parts are cast together for high efficiency by attaching individual wax patterns to a central wax stick called a sprue. The wax is melted out of the pattern – which is why it is also known as the lost wax process – and molten metal is poured into the cavity. When the metal solidifies, the ceramic mold is shaken off, leaving the near net shape of the desired casting, followed by CNC machining, testing and packaging.
What Are The Investment Castings Used For?
Investment castings are widely used in pumps and valves, automobile, trucks, hydraulics, forklift trucks and many other industries. Because of their exceptional casting tolerance and exellent finish, the lost wax castings are used more and more. Especially, the stainless steel investment castings play a vital important role in the shipbuilding and boats because they have strong anti-rust performance.
Casting Tolerance Could Reached by Investment Casting:
According to the different binder materials used for making the shell, the investment casting could be divided into silica sol casting and water glass casting. The silica sol investment casting process have better Dimensional Casting Tolerances (DCT) and Geometrical Casting Tolerances (GCT) than water glass process. However, even by same casting process, the Tolerance Grade will be different from each cast alloy due to their various castability. Our foundry would like to talk with you if you have special request on the required tolerances. Here in the following are the general tolerances grade we could reach both by silica sol casting and water glass casting processes separately:
- DCT Grade by Silica Sol Lost Wax Casting: DCTG4 ~ DCTG6
- DCT Grade by Water Glass Lost Wax Casting: DCTG5 ~ DCTG9
- GCT Grade by Silica Sol Lost Wax Casting: GCTG3 ~ GCTG5
- GCT Grade by Water Glass Lost Wax Casting: GCTG3 ~ GCTG5
|
Materials for Investment Casting Process at RMC Foundry |
|||
|
Category |
China Grade |
US Grade |
Germany Grade |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | 1Cr17, 022Cr12, 10Cr17, | 430, 431, 446, CA-15, CA6N, CA6NM | 1.4000, 1.4005, 1.4008, 1.4016, GX22CrNi17, GX4CrNi13-4 |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | 1Cr13, 2Cr13, 3Cr13, 4Cr13, | 410, 420, 430, 440B, 440C | 1.4021, 1.4027, 1.4028, 1.4057, 1.4059, 1.4104, 1.4112, 1.4116, 1.4120, 1.4122, 1.4125 |
| Austenitic stainless steel |
06Cr19Ni10, 022Cr19Ni10,
06Cr25Ni20, 022Cr17Ni12Mo2, 03Cr18Ni16Mo5
|
302, 303, 304, 304L, 316, 316L, 329, CF3, CF3M, CF8, CF8M, CN7M, CN3MN |
1.3960, 1.4301, 1.4305, 1.4306, 1.4308, 1.4313, 1.4321, 1.4401, 1.4403, 1.4404, 1.4405, 1.4406, 1.4408, 1.4409, 1.4435, 1.4436, 1.4539, 1.4550, 1.4552, 1.4581,
1.4582, 1.4584,
|
| Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel | 05Cr15Ni5Cu4Nb, 05Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb | 630, 634, 17-4PH, 15-5PH, CB7Cu-1 | 1.4542 |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | 022Cr22Ni5Mo3N, 022Cr25Ni6Mo2N | A 890 1C, A 890 1A, A 890 3A, A 890 4A, A 890 5A, A 995 1B, A 995 4A, A 995 5A, 2205, 2507 | 1.4460, 1.4462, 1.4468, 1.4469, 1.4517, 1.4770 |

 русский
русский



