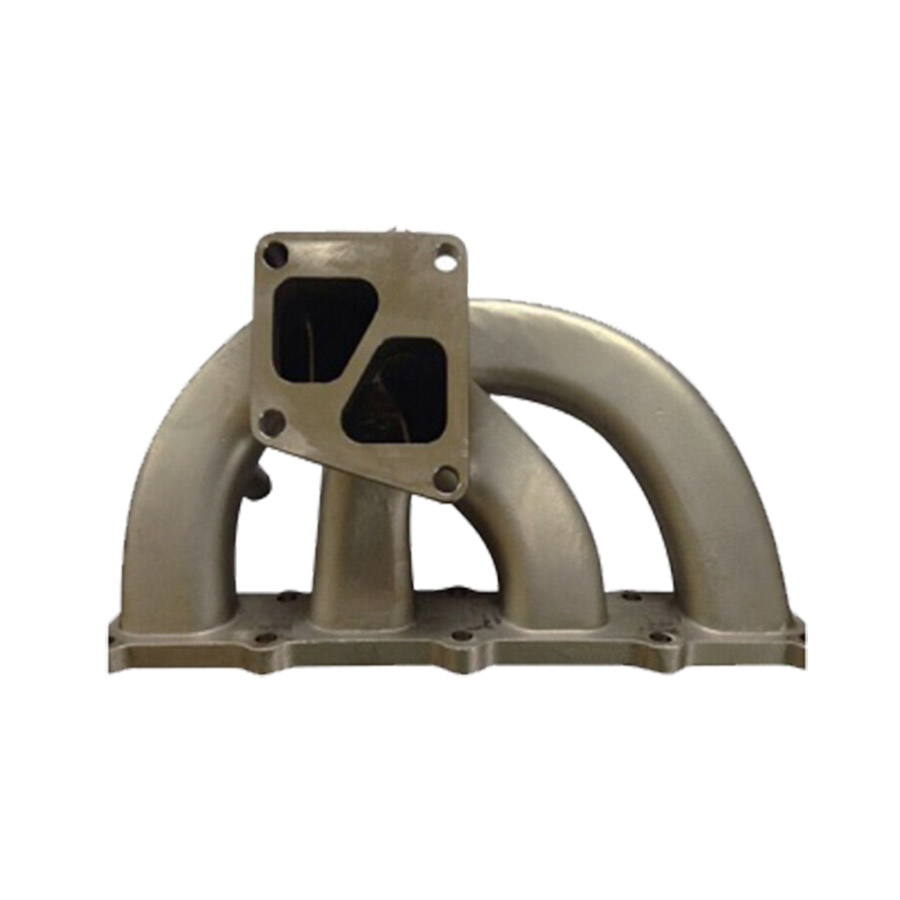

Stainless Steel Investment Casting Exhaust Manifold
Material: Cast Stainless Steel Process: Precision Investment Casting + CNC Machining Weight: 5.20 kg
China OEM custom stainless steel investment casting exhaust manifold with CNC machining services.
Custom stainless steel casting products produced by investment casting and CNC machining.
Investment casting, which is also known lost wax casting or precision casting, refers to the formation of ceramic around the wax patterns to create a multi or single part mold to receive molten metal. This process utilizes an expendable injection molded wax pattern process to achieve complex forms with exceptional surface qualities. To create a mold, a wax pattern, or cluster of patterns, is dipped into ceramic material several times to build a thick shell. De-wax process is then followed by the shell dry process. The wax-less ceramic shell is then produced. Molten metal is then poured into the ceramic shell cavities or cluster, and once solid and cooled, the ceramic shell is broken off to reveal the final cast metal object. Precision investment castings can achieve exceptional accuracy for both small and large casting parts in a wide range of materials.
| Investment Casting Technical Data at RMC Foundry | |
| R&D | Software: Solidworks, CAD, Procast, Pro-e |
| Lead Time for Development and Samples: 25 to 35 days | |
| Molten Metal | Ferritic Stainless Steel, Martensitic Stainless Steel, Austenitic stainless steel, Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel, Duplex Stainless Steel |
| Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Tool Steel, Heat Resistant Steel, | |
| Nickle-base Alloy, Aluminium Alloy, Copper-base Alloy, Cobalt-base Alloy | |
| Metal Standard | ISO, GB, ASTM, SAE, GOST EN, DIN, JIS, BS |
| Material for Shell Building | Silica Sol (Precipitated Silica ) |
| Water Glass (Sodium Silicate) | |
| Mixtures of Silica Sol and Water Glass | |
| Technical Parameter | Piece Weight: 2 gram to 200 kilo gram |
| Max Dimension: 1,000 mm for Diameter or Length | |
| Min Wall Thickness: 1.5mm | |
| Casting Roughness: Ra 3.2-6.4, Machining Roughness: Ra 1.6 | |
| Tolerance of Casting: VDG P690, D1/CT5-7 | |
| Tolerance of Machining: ISO 2768-mk/IT6 | |
| Inner Core: Ceramic Core, Urea Core, Water Soluble Wax Core | |
| Heat Treatment | Normalizing, Tempering, Quenching, Annealing, Solution, Carburization. |
| Surface Treatment | Polishing, Sand / Shot Blasting, Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating, Oxidation Treatment, Phosphating, Powder Painting, Geormet, Anodizing |
| Dimension Testing | CMM, Vernier Caliper, Inside Caliper. Depth Gage, Height Gage, Go/No go Gage, Special Fixtures |
| Chemical Inspection | Chemical Compostion Analysis (20 chemical elements), Cleanliness Inspection, X-ray Radiographic Inspection, Carbon-Sulfur Analyser |
| Physical Inspection | Dynamic Balancing, Static Blancing, Mechanical Properties (Hardness, Yield Strength, Tensile Strength), Elongation |
| Production Capacity | More than 250 tons per month, more than 3,000 tons annually. |
What Are The Advantages of Investment Casting?
✔ Excellent and smooth surface finish
✔ Tight dimensional tolerances.
✔ Complex and intricate shapes with design flexibility
✔ Capability to cast thin walls therefore a lighter casting component
✔ Wide selection of cast metals and alloys (ferrous and non-ferrous)
✔ Draft is not required in the molds design.
✔ Reduce the need for secondary machining.
✔ Low material waste.
| Equivalent Grade of Stainless Steel | |||||||
|
Types |
AISI | W-stoff | DIN | BS | SS | U.N.E. / I.H.A. | UNI |
| Martensitic and Ferritic Stainless Steel | 420 C | 1,4034 | X43Cr16 | ||||
| 440 B/1 | 1,4112 | X90 Cr Mo V18 | |||||
| - | 1.2083 | X42 Cr 13 | - | 2314 | F.5263 | - | |
| 403 | 1.4000 | X6Cr13 | 403 S 17 | 2301 | F.3110 | X6Cr13 | |
| (410S) | 1.4001 | X7 Cr 14 | (403 S17) | 2301 | F.3110 | X6Cr13 | |
| 405 | 1.4002 | X6 CrAl 13 | 405 S 17 | - | F.3111 | X6 CrAl 13 | |
| 416 | 1.4005 | X12 CrS 13 | 416 S 21 | 2380 | F.3411 | X12CrS13 | |
| 410 | 1.4006 | X 10 Cr 13 | 410 S21 | 2302 | F.3401 | X12Cr13 | |
| 430 | 1.4016 | X6 Cr 17 | 430 S 17 | 2320 | F.3113 | X8Cr17 | |
| 420 | 1.4021 | X20 Cr 13 | 420 S 37 | 2303 | F.3402 | X20Cr13 | |
| 420F | 1.4028 | X30 Cr 13 | 420 S 45 | (2304) | F.3403 | X30Cr13 | |
| (420) | 1.4031 | X39Cr13 | 420 S 45 | (2304) | F.3404 | - | |
| 431 | 1.4057 | X20 CrNi 17 2 | 431 S 29 | 2321 | F.3427 | X16CrNi16 | |
| 430F | 1.4104 | X12 CrMoS 17 | - | 2383 | F.3117 | X10CrS17 | |
| 434 | 1.4113 | X6 CrMo 17 | 434 S 17 | 2325 | - | X8CrMo17 | |
| 430Ti | 1.4510 | X6 CrTi 17 | - | - | - | X6CrTi17 | |
| 409 | 1.4512 | X5 CrTi 12 | 409 S 17 | - | - | X6CrTi12 | |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | 304 | 1.4301 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 15 | 2332 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 |
| 305 | 1.4303 | X5 CrNi 18 12 | 305 S 19 | - | - | X8CrNi19 10 | |
| 303 | 1.4305 | X12 CrNiS 18 8 | 303 S 21 | 2346 | F.3508 | X10CrNiS 18 09 | |
| 304L | 1.4306 | X2 CrNiS 18 9 | 304 S 12 | 2352 | F.3503 | X2CrNi18 11 | |
| 301 | 1.4310 | X12 CrNi 17 7 | - | 2331 | F.3517 | X12CrNi17 07 | |
| 304 | 1.4350 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 31 | 2332 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 | |
| 304 | 1.4350 | X5 CrNi 18 9 | 304 S 31 | 2333 | F.3551 | X5CrNi18 10 | |
| 304LN | 1.4311 | X2 CrNiN 18 10 | 304 S 62 | 2371 | - | - | |
| 316 | 1.4401 | X5 CrNiMo 18 10 | 316 S 16 | 2347 | F.3543 | X5CrNiMo17 12 | |
| 316L | 1.4404 | - | 316 S 12/13/14/22/24 | 2348 | X2CrNiMo17 12 | ||
| 316LN | 1.4429 | X2 CrNiMoN 18 13 | - | 2375 | - | - | |
| 316L | 1.4435 | X2 CrNiMo 18 12 | 316 S 12/13/14/22/24 | 2353 | - | X2CrNiMo17 12 | |
| 316 | 1.4436 | - | 316 S 33 | 2343 | - | X8CrNiMo 17 13 | |
| 317L | 1.4438 | X2 CrNiMo 18 16 | 317 S 12 | 2367 | - | X2CrNiMo18 16 | |
| 329 | 1.4460 | X3 CrNiMoN 27 5 2 | - | 2324 | F.3309 | - | |
| 321 | 1.4541 | X10 CrNiTi 18 9 | 321 S 12 | 2337 | F.3553 | X6CrNiTi18 11 | |
| 347 | 1.4550 | X10 CrNiNb 18 9 | 347 S 17 | 2338 | F.3552 | X6CrNiNb18 11 | |
| 316Ti | 1.4571 | X10 CrNiMoTi 18 10 | 320 S 17 | 2350 | F.3535 | X6CrNiMoTi 17 12 | |
| 309 | 1.4828 | X15 CrNiSi 20 12 | 309 S 24 | - | - | X16 CrNi 24 14 | |
| 330 | 1.4864 | X12 NiCrSi 36 16 | - | - | - | - | |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | S32750 | 1.4410 | X 2 CrNiMoN 25 7 4 | - | 2328 | - | - |
| S31500 | 1.4417 | X 2 CrNiMoSi 19 5 | - | 2376 | - | - | |
| S31803 | 1.4462 | X 2 CrNiMoN 22 5 3 | - | 2377 | - | - | |
| S32760 | 1.4501 | X 3 CrNiMoN 25 7 | - | - | - | - | |
| 630 | 1.4542 | X5CrNiCNb16-4 | - | - | - | - | |
| A564/630 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
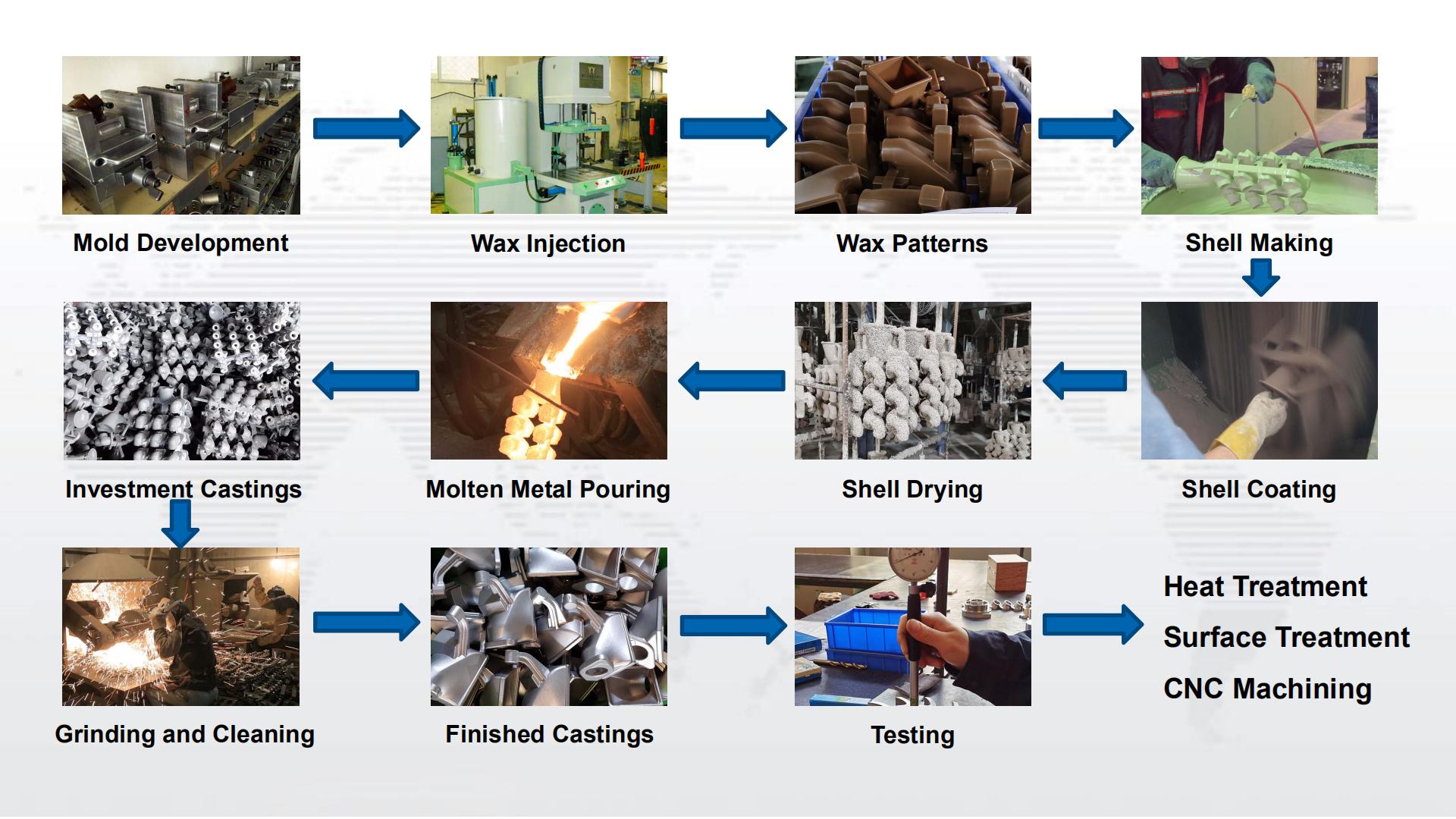
What Are The Steps of Investment Casting Process?
During the investment casting process, a wax pattern is coated with a ceramic material, which, when hardened, adopts the internal geometry of the desired casting. In most cases, multiple parts are cast together for high efficiency by attaching individual wax patterns to a central wax stick called a sprue. The wax is melted out of the pattern – which is why it is also known as the lost wax process – and molten metal is poured into the cavity. When the metal solidifies, the ceramic mold is shaken off, leaving the near net shape of the desired casting, followed by finishing, testing and packaging.
 русский
русский



