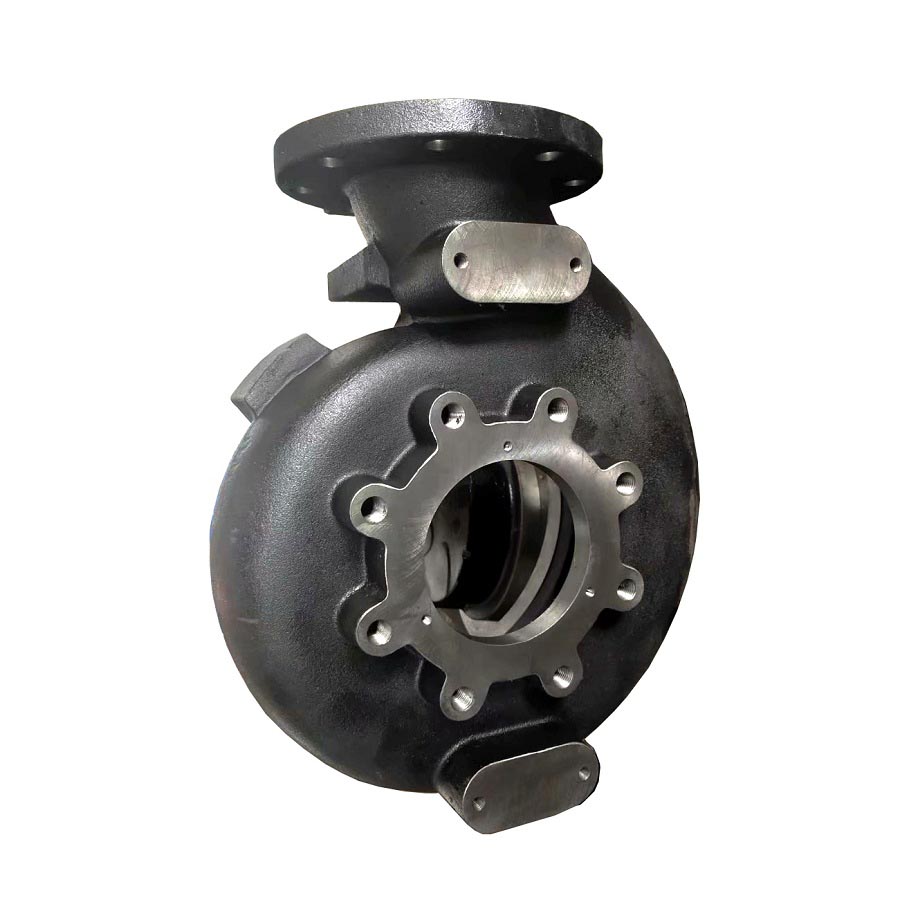

Ductile Cast Iron Investment Casting Pump Body / Housing
Material: Ductile Cast Iron EN-GJS-400-15 (GGG40) Process: Investment Casting + CNC Machining Weight: 15.26 kg Application: Pump Housing Surface Treatment: Painting / Powder Coating
China OEM custom ductile cast iron pump housing by investment casting and CNC machining. 3.1 material certificate is available if necessary.
Ductile Cast Iron Investment Castings for Centrifugal Pump Body with CNC Machining
Ductile cast iron would be cast by investment casting process if high accuracy is requested by the customers or end users. The investment castings of ductile iron would need less machining work than those by other casting processes such as green sand casting and shell mold casting.
Investment Casting Technical Data at RMC Foundry
R & D
Software: Solidworks, CAD, Procast, Pro-e
Lead Time for Development and Samples: 25 to 35 days
Molten Metal
Ferritic Stainless Steel, Martensitic Stainless Steel, Austenitic stainless steel, Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel, Duplex Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Tool Steel, Heat Resistant Steel,
Nickle-base Alloy, Aluminium Alloy, Copper-base Alloy, Cobalt-base Alloy
Metal Specifications
ISO, GB, ASTM, SAE, GOST EN, DIN, JIS, BS
Materials for Shell Building
Silica Solutions (Precipitated Silica )
Water Glass (Sodium Silicate)
Mixtures of Silica Sol and Water Glass
Technical Parameter
Piece Weight: 2 gram to 200 kilo gram
Max Dimension: 1,000 mm for Diameter or Length
Min Wall Thickness: 1.5mm
Casting Roughness: Ra 3.2-6.4, Machining Roughness: Ra 1.6
Tolerance of Casting: VDG P690, D1/CT5-7
Tolerance of Machining: ISO 2768-mk/IT6
Inner Core: Ceramic Core, Urea Core, Water Soluble Wax Core
Heat Treatment
Normalizing, Tempering, Quenching, Annealing, Solution, Carburization.
Surface Treatment
Polishing, Sand / Shot Blasting, Zinc Plating, Nickel Plating, Oxidation Treatment, Phosphating, Powder Painting, Geormet, Anodizing
Dimension Testing
CMM, Vernier Caliper, Inside Caliper. Depth Gage, Height Gage, Go/No go Gage, Special Fixtures
Chemical Inspection
Chemical Compostion Analysis (20 chemical elements), Cleanliness Inspection, X-ray Radiographic Inspection, Carbon-Sulfur Analyser
Mechanical Properties Inspection
Dynamic Balancing, Static Blancing, Mechanical Properties (Hardness, Yield Strength, Tensile Strength), Elongation
Production Capacity
More than 250 tons per month, more than 3,000 tons annually.
Ductile iron, which is also known as ducitle cast iron, nodular iron, spheroidal graphite iron, spheroidal graphite cast iron, or just SG iron for short. When graphite is present as small, round, and well-distributed particles, its weakening effect is small and such cast irons would have higher ductility. This type of cast iron is called ductile or nodular iron or spheroidal graphite or simply SG iron. This form of graphite can be achieved by adding elemental magnesium or cerium or a combination of the two elements to molten cast iron. Magnesium is added in quantities of 0.07 to 0. 10% followed by the addition of ferro-silicon to promote graphitization. During solidification, magnesium helps in the distribution of graphite throughout the metal.
Ductile iron has better strength-to-weight ratio, better machinability and higher impact value. Moreove, the ductile iron components are produced by casting process wherein better control of component shape can be achieved compared to drop forging. Thus, many a component such as crank shafts and connecting rods manufactured usually by drop forging is increasingly being replaced by ductile iron castings.
Investment (lost wax) casting is a method of precision casting complex near-net-shape details using replication of wax patterns. Investment casting or lost wax is a metal forming process that typically uses a wax pattern surrounded by a ceramic shell to make a ceramic mold. When the shell dries, the wax is melted away, leaving only the mold. Then the casting component is formed by pouring molten metal into the ceramic mold.
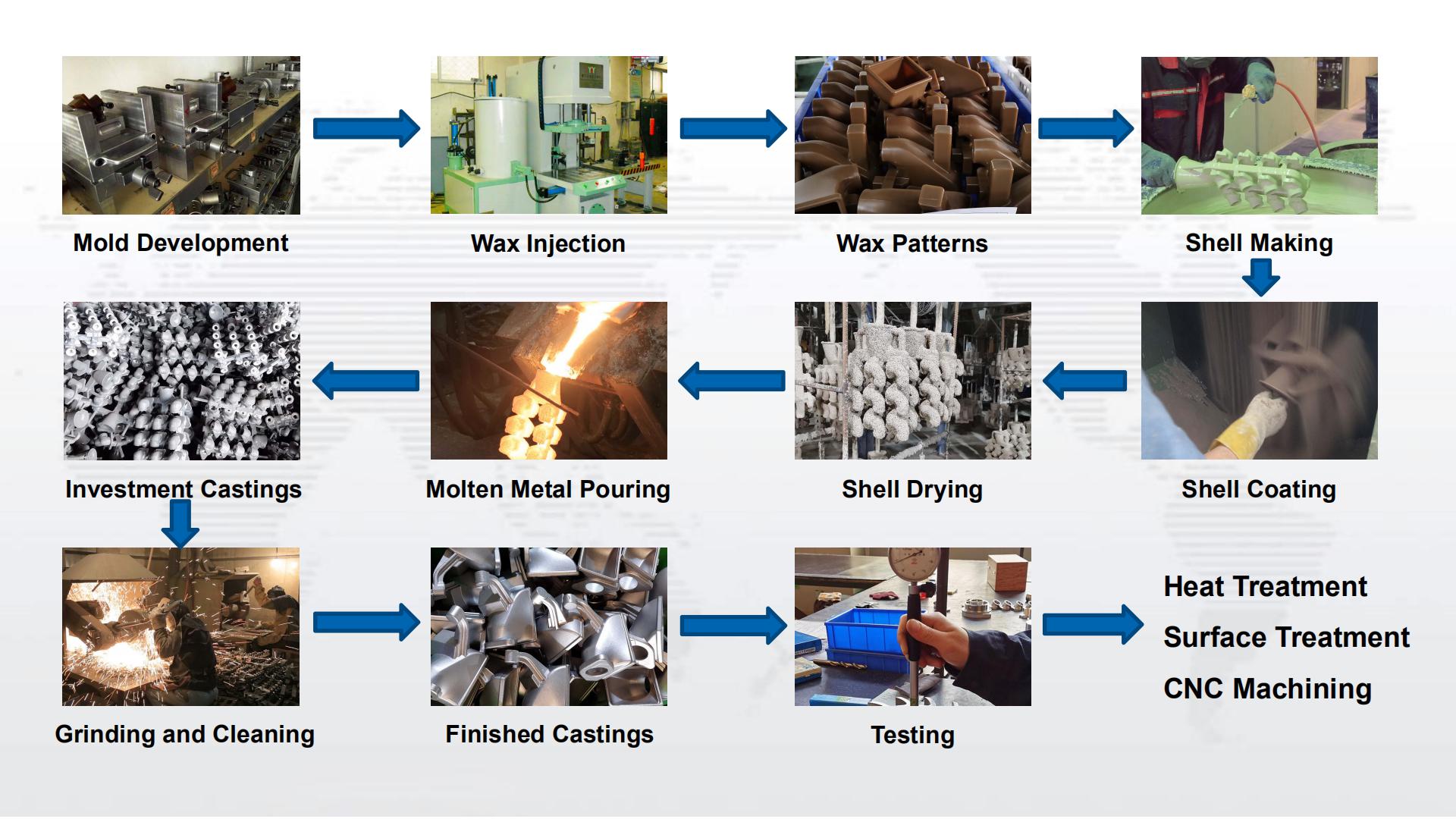
Ductile (Nodular) cast iron obtains nodular graphite through spheroidization and inoculation treatment, which effectively improves the mechanical properties of the cast iron, especially the plasticity and toughness, so as to obtain higher strength than carbon steel. Nodular cast iron is a high-strength cast iron material developed in the 1950s. Its comprehensive properties are close to steel. Based on its excellent properties, the ductile iron has been successfully used for casting components of complex forces, strength, toughness and wear resistance. Nodular cast iron has rapidly developed into a cast iron material second only to gray cast iron and widely used. The so-called "substituting iron for steel" mainly refers to ductile iron. Ductile iron is often used to produce parts for crankshafts and camshafts for automobiles, tractors, and internal combustion engines, as well as medium-pressure valves for general machinery.
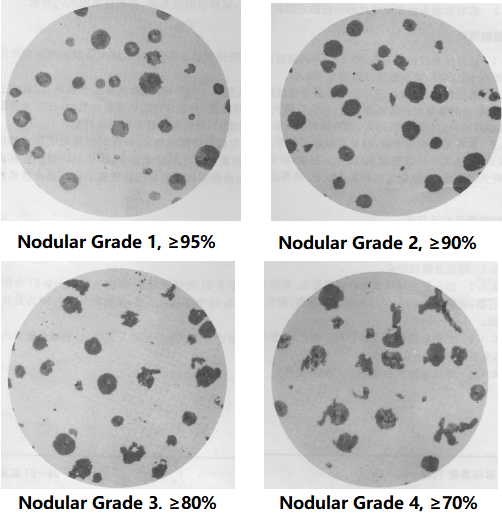

Ductile iron is not a single material but is part of a group of materials which can be produced to have a wide range of properties through control of the microstructure. The common defining characteristic of this group of materials is the shape of the graphite. In ductile irons, the graphite is in the form of nodules rather than flakes as it is in grey iron. The sharp shape of the flakes of graphite create stress concentration points within the metal matrix and the rounded shape of the nodules less so, thus inhibiting the creation of cracks and providing the enhanced ductility that gives the alloy its name. The formation of nodules is achieved by the addition of nodulizing elements, most commonly magnesium (note magnesium boils at 1100°C and iron melts at 1500°C) and, less often now, cerium (usually in the form of Mischmetal). Tellurium has also been used. Yttrium, often a component of Misch metal, has also been studied as a possible nodulizer.
| Ductile Iron Grade from Different Countries | ||||||||||
| No. | China | Japan | U.S.A. | ISO | German | France | Russia гост | U.K. BS | ||
| GB | JIS | ASTM | UNS | DIN | W-Nr. | NF | ||||
| 1 | FCD350-22 | - | - | 350-22 | - | - | - | Bч35 | 350/22 | |
| 2 | QT400-15 | FCD400-15 | - | - | 400-15 | GGG-40 | 0.7040 | EN-GJS-400-15 | Bч40 | 370/17 |
| 3 | QT400-18 | FCD400-18 | 60-40-18 | F32800 | 400-18 | - | - | EN-GJS-400-18 | - | 400/18 |
| 4 | QT450-10 | FCD450-10 | 65-45-12 | F33100 | 450-10 | - | - | EN-GJS-450-10 | Bч45 | 450/10 |
| 5 | QT500-7 | FCD500-7 | 80-55-6 | F33800 | 500-7 | GGG-50 | 0.7050 | EN-GJS-500-7 | Bч50 | 500/7 |
| 6 | QT600-3 | FCD600-3 | ≈80-55-06 ≈100-70-03 | F3300 F34800 | 600-3 | GGG-60 | 0.7060 | EN-GJS-600-3 | Bч60 | 600/3 |
| 7 | QT700-2 | FCD700-2 | 100-70-03 | F34800 | 700-2 | GGG-70 | 0.7070 | EN-GJS-700-2 | Bч70 | 700/2 |
| 8 | QT800-2 | FCD800-2 | 120-90-02 | F36200 | 800-2 | GGG-80 | 0.7080 | EN-GJS-800-2 | Bч80 | 800/2 |
| 8 | QT900-2 | 120-90-02 | F36200 | 800-2 | GGG-80 | 0.7080 | EN-GJS-900-2 | ≈Bч100 | 900/2 | |

 русский
русский



