The heat treatment of steel castings is based on the Fe-Fe3C phase diagram to control the microstructure of the steel castings to achieve the required performance. Heat treatment is one of the important processes in the production of steel castings. The quality and effect of heat treatment are directly related to the final performance of steel castings.
The as-cast structure of steel castings depends on the chemical composition and solidification process. Generally, there are relatively serious dendrite segregation, very uneven structure and coarse grains. Therefore, steel castings generally need to be heat treated to eliminate or reduce the impact of the above problems, so as to improve the mechanical properties of steel castings. In addition, due to the difference in the structure and wall thickness of the steel castings, various parts of the same casting have different organizational forms and generate considerable residual internal stress. Therefore, steel castings (especially alloy steel castings) should generally be delivered in a heat-treated state.
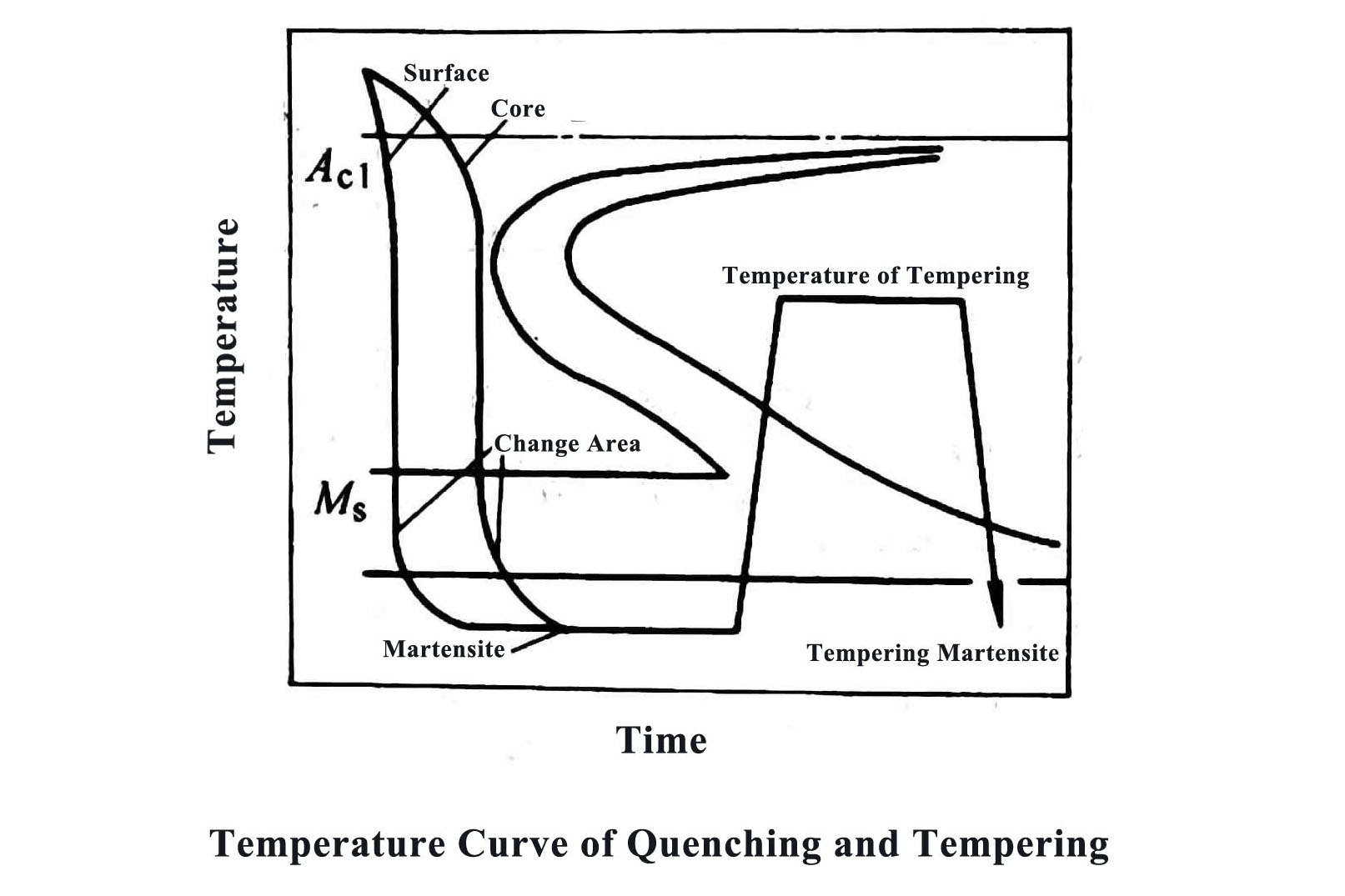
1. The Characteristics of The Heat Treatment of Steel Castings
1) In the as-cast structure of steel castings, there are often coarse dendrites and segregation. During the heat treatment, the heating time should be slightly higher than that of the forging steel parts of the same composition. At the same time, the holding time of austenitization needs to be appropriately extended.2) Due to the serious segregation of the as-cast structure of some alloy steel castings, in order to eliminate its influence on the final properties of the castings, measures should be taken to homogenize during heat treatment.
3) For steel castings with complex shapes and large wall thickness differences, cross-sectional effects and casting stress factors must be considered during heat treatment.
4) When heat treatment is performed on steel castings, it must be reasonable based on its structural characteristics and try to avoid deformation of the castings.
2. The Main Process Factors of the Heat Treatment of Steel Castings
The heat treatment of steel castings consists of three stages: heating, heat preservation, and cooling. The determination of process parameters should be based on the purpose of ensuring product quality and saving costs.1) Heating
Heating is the most energy-consuming process in the heat treatment process. The main technical parameters of the heating process are to select an appropriate heating method, heating speed and charging method.
(1) Heating method. The heating methods of steel castings mainly include radiant heating, salt bath heating and induction heating. The selection principle of heating method is fast and uniform, easy to control, high efficiency and low cost. When heating, the foundry generally considers the structural size, chemical composition, heat treatment process and quality requirements of the casting.
(2) Heating speed. For general steel castings, the heating speed may not be limited, and the maximum power of the furnace is used for heating. The use of hot furnace charging can greatly shorten the heating time and production cycle. In fact, under the condition of rapid heating, there is no obvious temperature hysteresis between the surface of the casting and the core. Slow heating will result in reduced production efficiency, increased energy consumption, and serious oxidation and decarburization on the surface of the casting. However, for some castings with complex shapes and structures, large wall thicknesses, and large thermal stresses during the heating process, the heating speed should be controlled. Generally, low temperature and slow heating (below 600 °C) or staying at low or medium temperature can be used, and then rapid heating can be used in high temperature areas.
(3) Loading method. The principle that steel castings should be placed in the furnace is to make full use of the effective space, ensure uniform heating and place the castings to deform.2) Insulation
The holding temperature for austenitization of steel castings should be selected according to the chemical composition of the cast steel and the required properties. The holding temperature is generally slightly higher (about 20 °C) than forging steel parts of the same composition. For eutectoid steel castings, it should be ensured that carbides can be quickly incorporated into austenite, and that the austenite can maintain fine grains.
Two factors should be considered for the heat preservation time of steel castings: the first factor is to make the temperature of the casting surface and the core uniform, and the second factor is to ensure the uniformity of the structure. Therefore, the holding time mainly depends on the thermal conductivity of the casting, the wall thickness of the section and the alloy elements. Generally speaking, alloy steel castings require longer holding time than carbon steel castings. The wall thickness of the casting is usually the main basis for calculating the holding time. For the holding time of tempering treatment and aging treatment, factors such as the purpose of heat treatment, holding temperature and element diffusion rate should be considered.
3) Cooling
The steel castings can be cooled at different speeds after heat preservation, in order to complete the metallographic transformation, obtain the required metallographic structure and achieve the specified performance indicators. Generally speaking, increasing the cooling rate can help to obtain a good structure and refine the grains, thereby improving the mechanical properties of the casting. However, if the cooling rate is too fast, it is easy to cause greater stress in the casting. This may cause deformation or cracking of castings with complex structures. The cooling medium for the heat treatment of steel castings generally includes air, oil, water, salt water and molten salt.
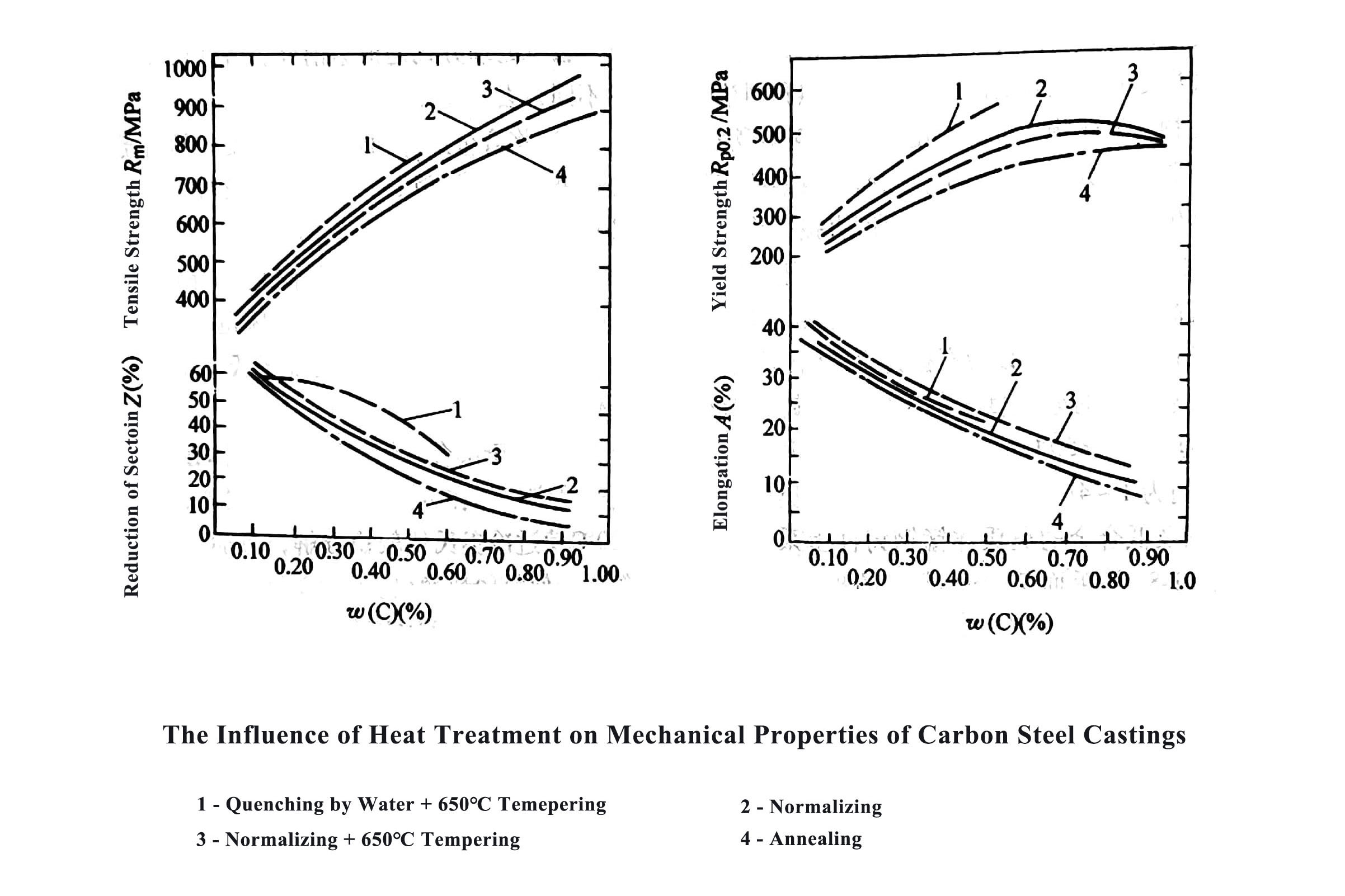
3. The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Properties of Steel Castings
In addition to the performance of steel castings depending on the chemical composition and casting process, different heat treatment methods can also be used to make it have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties. The general purpose of the heat treatment process is to improve the quality of the castings, reduce the weight of the castings, extend the service life and reduce costs. Heat treatment is an important means to improve the mechanical properties of castings; the mechanical properties of castings are an important indicator for judging the effect of heat treatment. In addition to the following properties, the foundry must also consider factors such as processing procedures, cutting performance and the use requirements of the castings when heat-treating steel castings.
1) The Influence of Heat Treatment on the Strength of Castings
Under the condition of the same cast steel composition, the strength of steel castings after different heat treatment processes has a tendency to increase. Generally speaking, the tensile strength of carbon steel castings and low alloy steel castings can reach 414 Mpa-1724 MPa after heat treatment.
2) The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Plasticity of Steel Castings
The as-cast structure of the steel castings is coarse and the plasticity is low. After heat treatment, its microstructure and plasticity will be improved accordingly. Especially the plasticity of steel castings after quenching and tempering treatment (quenching + high temperature tempering) will be significantly improved.
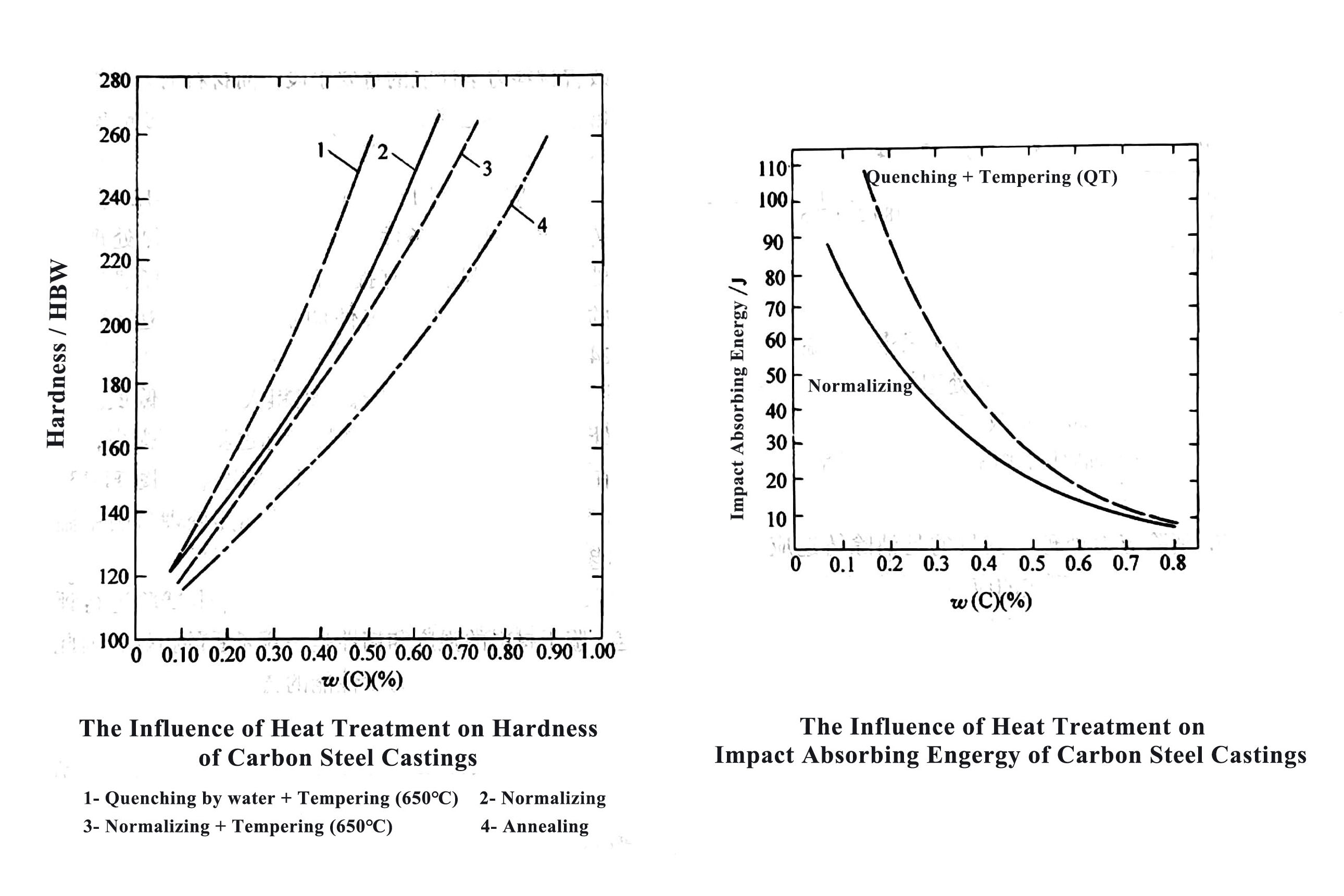
3) Toughness of Steel Castings
The toughness index of steel castings is often evaluated by impact tests. Since the strength and toughness of steel castings are a pair of contradictory indicators, the foundry must make comprehensive considerations to select a suitable heat treatment process in order to achieve the comprehensive mechanical properties required by customers.
4) The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Hardness of Castings
When the hardenability of the cast steel is the same, the hardness of the cast steel after heat treatment can roughly reflect the strength of the cast steel. Therefore, the hardness can be used as an intuitive index to estimate the performance of cast steel after heat treatment. Generally speaking, the hardness of carbon steel castings can reach 120 HBW - 280 HBW after heat treatment.
 русский
русский



